From Restrooms to Press Box: The Hidden Automation Behind the Scenes
Why stadium automation is different
- Occupancy can jump from zero to tens of thousands in under two hours
- Systems must perform flawlessly without warm-up or manual adjustment
- Multiple building systems must coordinate simultaneously, not sequentially
- Failures are immediate, public, and disruptive to the event experience
When tens of thousands of fans arrive within a narrow window, a stadium becomes one of the most demanding buildings in the world to operate. Occupancy spikes instantly. Loads shift continuously. Systems that sit idle for days must perform flawlessly for hours–without hesitation, delay, or visible failure.
Stadiums are a stress test for building automation. Unlike offices or campuses, there is no gradual ramp-up, no margin for manual adjustment, and no tolerance for systems that respond too slowly. If automation isn’t designed to anticipate demand and coordinate systems in real time, the breakdown is immediate—and highly visible.
Fans will remember the score, the big plays, and the halftime show.
But they likely won’t remember the building—and that’s the goal.
That seamless experience is powered by building automation systems working quietly behind the scenes, coordinating HVAC, ventilation, lighting, power, water, and fire and safety systems across the entire stadium. When BAS does its job well, there are no timeouts for building issues—just uninterrupted play and happy fans.
Stadiums: The ultimate stress test for building automation
Stadiums are among the most demanding environments a BAS can serve. Facilities like Levi’s Stadium span roughly 1.8 million square feet, with hundreds of thousands of square feet of enclosed, conditioned space—and occupancy that can jump from zero to more than 68,000 people in less than two hours.
To manage that swing while meeting strict California energy standards, BAS relies on dense networks of sensing and control. Zone- and duct-level temperature sensors provide continuous feedback across concourses, suites, and support spaces. At the zone level, programmable controllers like the KMC BAC-4000 Appstat Series manage airflow and temperature so systems respond dynamically without wasting energy during downtime.
Restrooms: Where demand spikes first and automation is immediately tested
Restrooms are one of the highest-impact spaces in a stadium. When play pauses on the field, restrooms experience extreme spikes in usage, require constant ventilation, and must remain comfortable despite doors opening continuously and humidity levels changing rapidly. At the same time, water systems have to keep pace—toilets must flush reliably, sinks need consistent pressure and temperature, and everything has to work without hesitation when demand peaks.
Without responsive automation, restrooms tend to fail in predictable ways. Ventilation systems are often oversized and left running continuously to prepare for peak demand, wasting energy during long periods of downtime. Or they fall behind during surges, allowing odors, humidity, and discomfort to build quickly.
Automation allows restroom systems to respond immediately to demand while supporting sustainability goals. Temperature and humidity transmitters—such as Greystone Humidity Sensors—help drive ventilation strategies that control odors and moisture during peak periods. Behind the scenes, control power components support valves, sensors, and automation hardware that ensure hot water is available when fans need it, without running systems unnecessarily between events.
Press boxes and club suites: Precision control in high-expectation spaces
Press boxes and premium suites demand tighter environmental control than general seating areas. These spaces are occupied longer, house luxury accessories, and carry higher expectations for comfort and air quality.
BAS enables these areas to operate independently from the rest of the stadium. High-accuracy temperature and humidity sensing feeds zone-level controllers that maintain steady conditions regardless of outdoor weather or crowd behavior elsewhere in the venue. The result is consistent comfort without over-conditioning surrounding spaces.
HVAC at scale: Ramping from empty to sold out without missing a beat
At stadium scale, HVAC automation must handle:
- Rapid ramp-up before gates open
- Constant load shifts as crowds move
- Large duct systems with variable pressure demands
- Fast scale-down immediately after events end
Few buildings experience occupancy swings like a stadium. HVAC systems must ramp up quickly for event days, then scale back just as efficiently once the crowd leaves.
That flexibility depends on automation. Actuators like Schneider Electric’s MS SmartX Series provide precise, automated control for dampers in HVAC systems, helping to regular airflow and maintain building comfort and energy efficiency. Static and differential pressure transmitters—such as the Belimo 22ADP Series—also help maintain proper airflow through large duct systems as loads change. Using smart BAS products like these enable operators to prepare in advance, rather than reacting after tens of thousands of fans arrive.
Parking garages and loading docks: Safety starts before fans enter
In these spaces, automation must balance:
- Continuous air quality monitoring
- Rapid response to exhaust buildup
- Compliance with safety thresholds
- Energy efficiency during long idle periods
Before fans ever reach the gates, BAS is already at work in parking garages and loading docks. These areas must be monitored continuously for vehicle exhaust and ventilated only when conditions require it.
Carbon monoxide and nitrogen dioxide gas detectors, including CO and NO₂ sensors, track exhaust from gas and diesel vehicles in real time. Kele offers a wide range of gas and specialty sensors. When levels exceed safe thresholds, BAS automatically enables ventilation systems—and then scales them back once air quality returns to acceptable levels—protecting occupants while minimizing unnecessary energy use.
Equipment and mechanical rooms: The operational backbone of stadium automation
Mechanical rooms are the nerve centers of stadium automation. Panels housing controllers, relays, transformers, and termination points are often installed in tight spaces near occupied areas, making reliability and serviceability critical.
Control transformers like the Functional Devices RIB TR Series provide stable power for controllers, sensors, and relays throughout the building. Well-organized panels allow technicians to wire, terminate, and maintain BAS components efficiently, ensuring all systems—from HVAC to lighting to safety—work together as intended. Kele not only offers panel components, but builds hundreds of complete panels to specs supplied by our customers, ready to install.
The field: Automation that protects playability and safety
The playing surface itself depends on automation to remain safe and playable. Stadium systems manage lighting, irrigation, drainage, and even subsurface ventilation and heating.
Water detection devices, such as Kele’s popular WD-2 Leak Detector, plus multiple other leak detection options, help identify drainage or moisture issues early. Integrated controls coordinate lighting schedules and field ventilation systems that heat, cool, and dry the surface, extending playability in extreme weather and reducing recovery time between events.
Concessions: Coordinating systems for instantaneous demand
During peak demand, concession areas require coordination between:
- Kitchen and exhaust ventilation
- Pumps and domestic hot water systems
- Ice machines, refrigeration, and electrical loads
- Safety systems managing heat and moisture
Concessions are a coordination challenge unlike almost anywhere else in the stadium. When play stops, demand spikes instantly—and kitchens, ventilation systems, pumps, ice machines, and domestic hot water equipment all need to come online in the right sequence. These systems aren’t just supporting food service; they’re also managing heat, moisture, and safety in some of the most densely occupied spaces in the venue.
Building automation makes that orchestration possible. Relays and control power components—such as Functional Devices Enclosed Relays—automatically enable exhaust fans, grease control systems, pumps, and ice makers as concession zones are activated, removing the need for manual sequencing. By coordinating multiple systems at once, BAS helps keep food moving, equipment protected, and lines flowing during the busiest moments of the event.
Beyond game day: Adapting automation for concerts and special events
Stadiums host far more than games. Concerts and special events introduce a different set of challenges, including pyrotechnics, theatrical smoke effects, and changing occupancy patterns that can place new demands on ventilation and life safety systems.
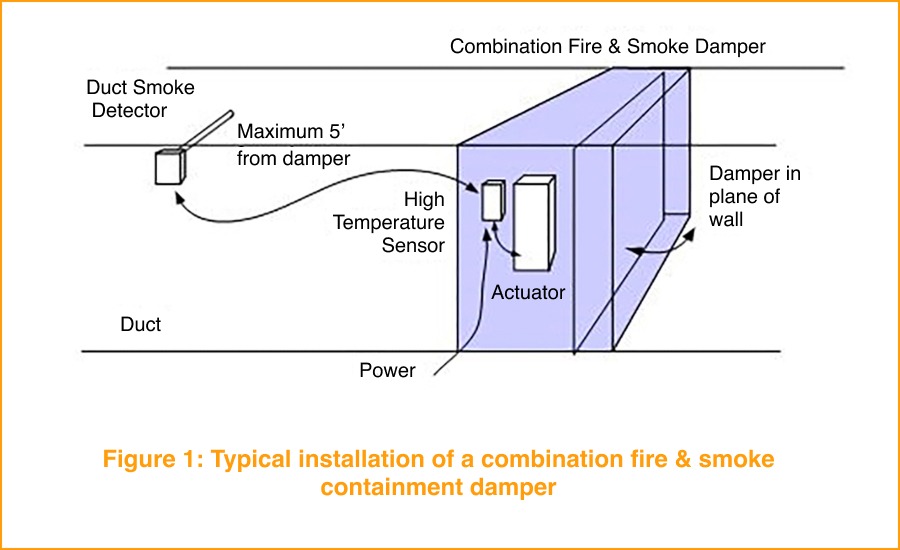
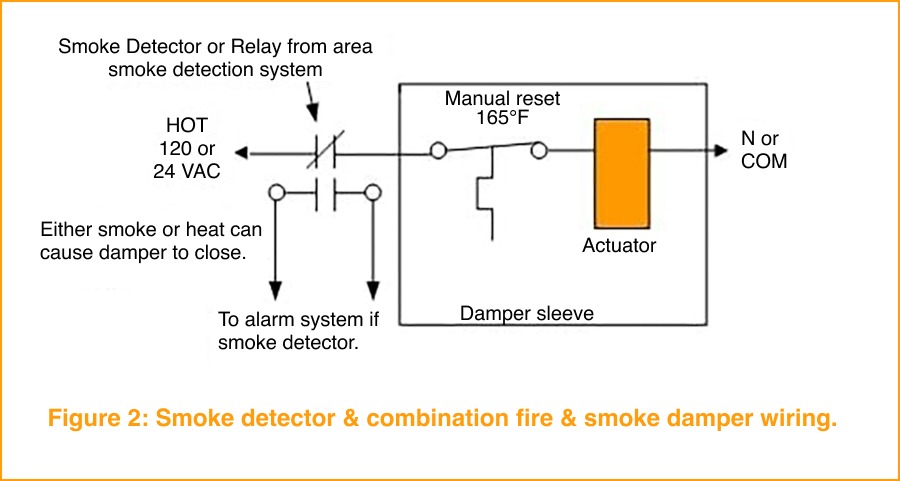
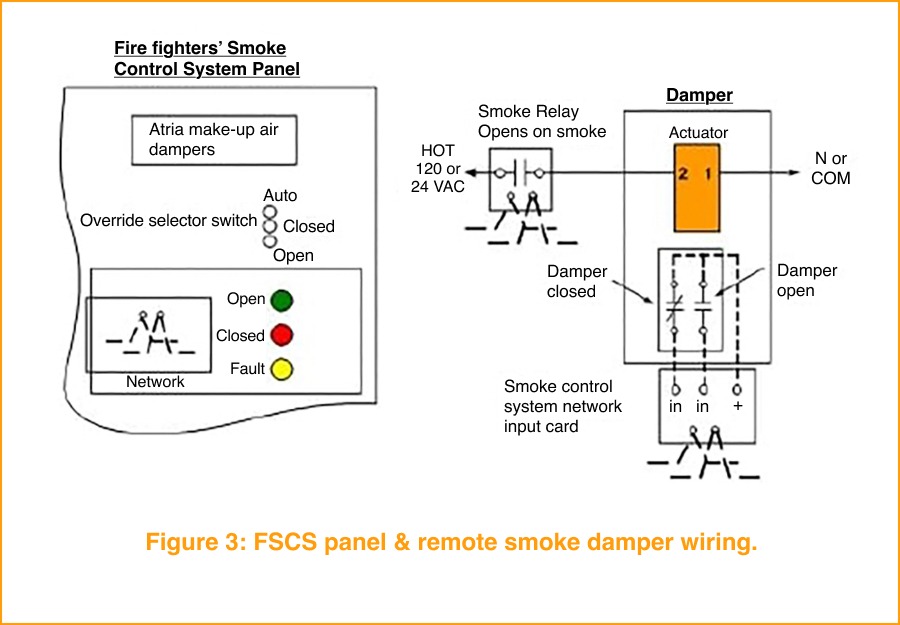
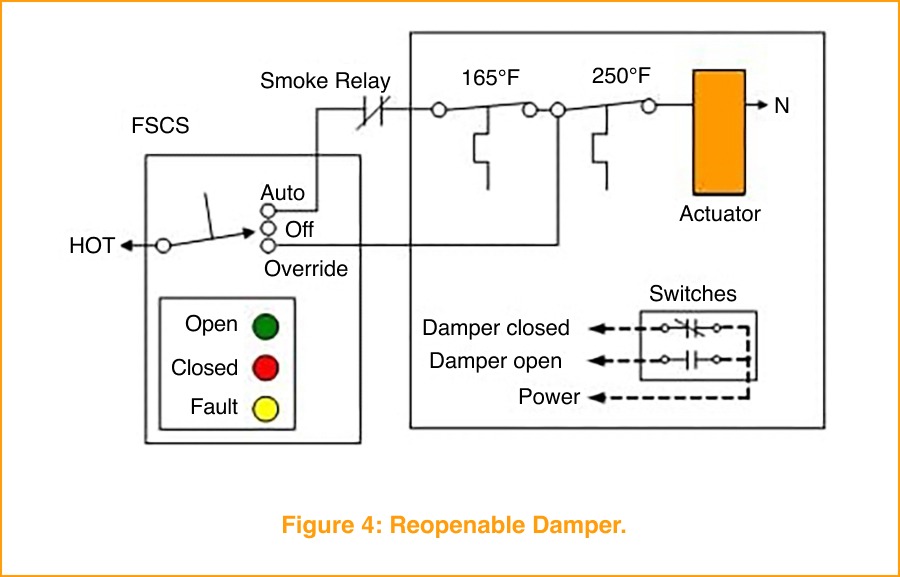
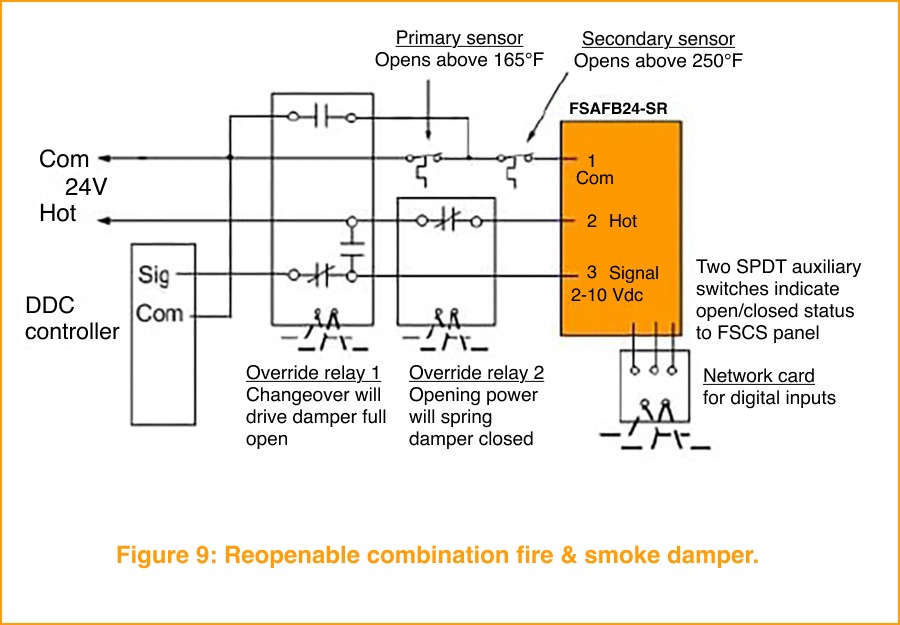
Building automation allows venues to reconfigure quickly for these events. Smoke control strategies coordinate fans, dampers, and ventilation systems to clear smoke from enclosed spaces efficiently, while fire and smoke damper actuators—such as the Belimo FS Series—integrate with BAS and life safety systems to support engineered smoke-control sequences. This coordination helps ensure visibility, air quality, and safety are maintained throughout the event, without disrupting the experience for performers or fans.
Delivering this level of coordination requires more than individual components. Stadium automation systems must be designed, specified, and bid with integration in mind from the start. Decisions made early around sensing density, control strategies, power requirements, and panel design determine whether systems will work together seamlessly once the venue is live.
One interface, total visibility across a complex venue
The real power of BAS lies in integration. Operators shouldn’t have to log in and out of separate systems to manage HVAC, lighting, security, fire safety, and water systems. A unified interface brings all of those systems together, giving facility teams real-time visibility across the entire venue so they can make informed decisions, enable equipment proactively, and maintain comfort and safety without disruption.
This level of coordination doesn’t happen by accident. Kele works closely with customers who design, bid, and build these integrated automation systems—often supplying the bill of materials needed to support competitive bids. Once those projects are awarded, those same components become the backbone of systems that monitor and control much of the facility, from enabling ventilation and pumps to managing water heat exchange and HVAC operation. In many stadium projects, these integrated systems account for up to 90% of the building’s operational infrastructure—all accessible from a single, centralized platform.
Energy, sustainability, and the bigger picture
Stadiums make the stakes of building automation unmistakable. Systems must scale instantly, perform under pressure, and disappear into the background while still meeting energy, sustainability, and regulatory demands. Stadiums must reduce waste during downtime, meet increasingly strict regulatory requirements, and demonstrate measurable improvements year over year—all while delivering a seamless experience on event day. For fans and players alike, comfort, air quality, and safety are simply expected, even as conditions change rapidly and demand spikes without warning.
That balance is exactly what building automation makes possible. By coordinating systems behind the scenes, BAS allows venues to scale up when it matters and scale back when it doesn’t—protecting energy budgets without compromising the experience. And while stadiums represent one of the most demanding use cases, the same BAS strategies apply across hospitals, campuses, arenas, convention centers, and large corporate headquarters. The scale may change, but the objective remains the same: deliver comfort, reliability, and efficiency at all times—so occupants can focus on what they’re there for, without ever noticing the systems making it all work.






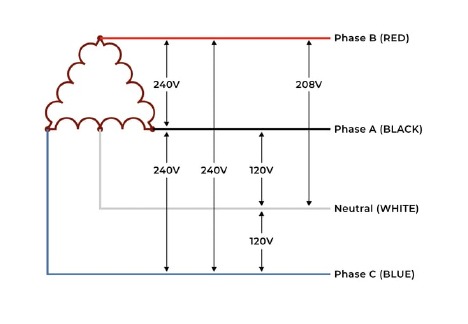
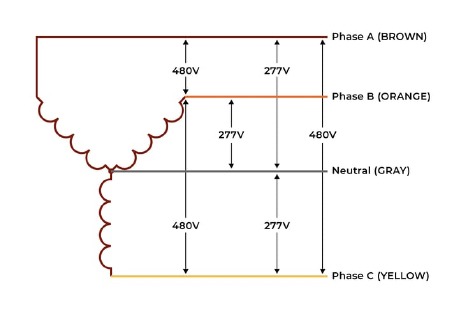
 Let’s say you want to connect the delta configuration to our TR50VA015. If you wanted to connect 120 Vac to the primary, you would connect your neutral (WHITE) to the transformer Comm (Blk). Then you would either connect phase A or C (BLACK or BLUE) to the 120 Vac tap on the transformer (Wht). If you wanted to use 240 Vac on the primary, you would take any two of the three phases and connect them to the orange and black wires on the transformer. It doesn’t matter which phase goes to which wire.
Let’s say you want to connect the delta configuration to our TR50VA015. If you wanted to connect 120 Vac to the primary, you would connect your neutral (WHITE) to the transformer Comm (Blk). Then you would either connect phase A or C (BLACK or BLUE) to the 120 Vac tap on the transformer (Wht). If you wanted to use 240 Vac on the primary, you would take any two of the three phases and connect them to the orange and black wires on the transformer. It doesn’t matter which phase goes to which wire.